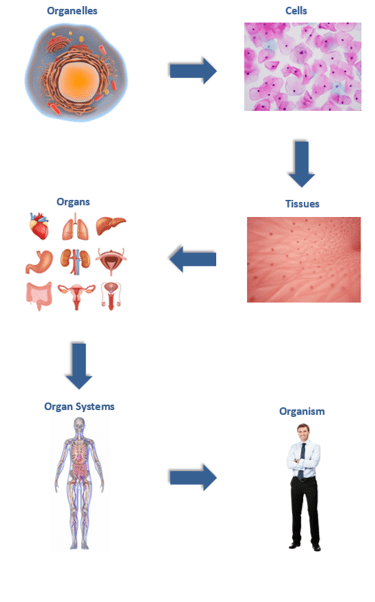
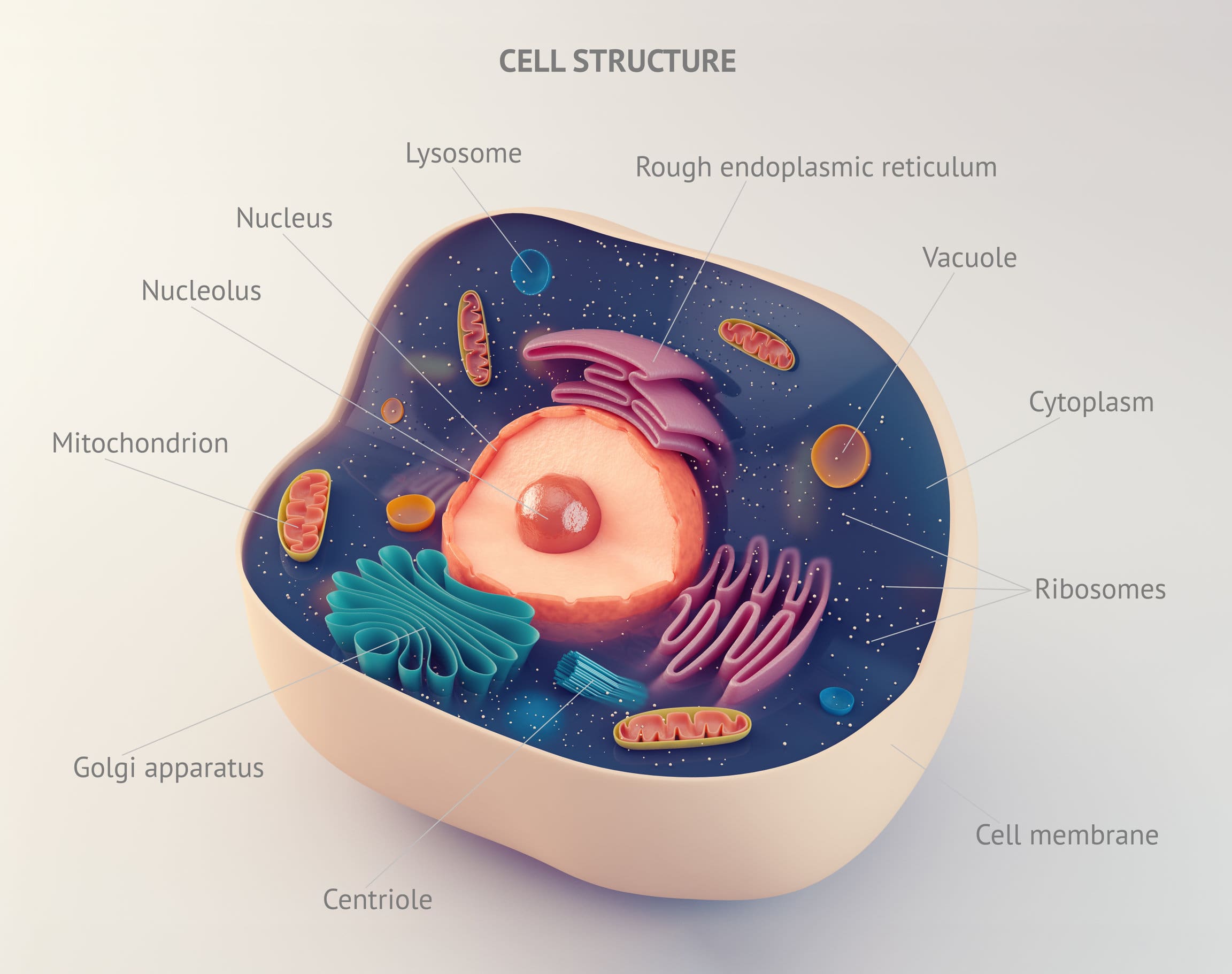
Living organisms are either multicellular (made up of more than one cell) or are unicellular (made up of just one cell). Most cells contain a number of organelles that have specific functions (refer back to Topic 1 in case you need to recap the ‘typical’ cell structures of the different five kingdoms of living organisms); however, we have not gone into much detail about the levels of organisation in between the cell and the organism. The levels of organisation in multicellular organisms are: organelles → cells → tissues → organs → organ systems → living organism.
| Structure | Description |
|---|---|
| Organelles | A structure that performs specific functions within a cell. Examples of different types of organelles include: a nucleus, mitochondrion, lysosome etc. |
| Cells | The basic functional and structural unit of a living organism. Examples of different types of cells include: blood cells, skin cells, bone cells etc. |
| Tissues | Cells with similar functions are grouped together as tissues. Together the cells perform a shared function. For example, the muscles in an animal’s leg contain millions of similar muscle cells which group together to perform a shared function; the contraction to move the leg bones. Tissues make up organs. A single organ can be made up of a number of different types of tissues. For example, the stomach is an organ that contains muscular tissue which has a role in the process of peristalsis; glandular tissue which produces digestives juices e.g. acid and enzymes; and epithelial which cover the inner and outer surfaces of the stomach. |
| Organs | Organs are formed by the functional grouping of multiple tissues. Examples of different organs include: the heart, lungs, pancreas, liver etc. |
| Organ systems | Organ systems are made up of a group of organs that work together to perform specific body functions. Examples of different organ systems include: cardiovascular system, digestive system, endocrine system, respiratory system, nervous system etc. |
| Living organism | A living organism is any living system. Living organisms are split into five kingdoms: animals (including humans), plants, fungi, protoctists and bacteria. |
Look at the following diagram which offers a detailed illustration of the level of organism in reference to animals.